Case Studies
For over a decade, we have continued to learn and deliver innovative solutions in areas spanning decarbonisation, energy conversion, emissions reduction, air quality, materials and process design, urbanisation and mobility. We deliver interoperability across data, software, models and domains to solve cross-sector challenges.
Explore our work and case studies via live demos, project overviews and user stories.
For further information on our work, feel free to contact us.
Alternatively, visit The World Avatar™ website.
Demos
CMCL have both developed and contributed to a number of live demos utilising The World Avatar™. A selection of these demos have been made publically available via the website, and can be accessed via the interactive network below.
Projects
The World Avatar™ can be utilised to serve different needs across a multitude of domains, and handle data at a variety of scales. Listed below are details on a number of collaborative projects and direct consultations in which The World Avatar™ was deployed to successfully help deliver on the project’s deliverables and/or customer’s needs.
Listed below are some of the projects that CMCL has been working on recently, with more information, reports and demos available via the links.
The Climate Resilience Demonstrator, CReDo, is a climate change adaptation digital twin demonstrator project developed by the National Digital Twin programme to improve resilience across infrastructure networks.
The Digital Open Marketplace Ecosystem (DOME) 4.0 project intends to offer an intelligent semantic industrial data ecosystem for knowledge creation across the entire materials to manufacturing value chains. CMCL are the overall project co-ordinators.
The DE-WASTE project is a collaboration between CMCL and Singaporean waste services company BNL. Digitalising their operations and connecting to external sectors will allow them to receive better insights into their operations and thus make better-informed decisions.
Sectors

NEED
CMPG is currently supporting the NEED project, (NEuE Daten für die Energiewende or New Data for the Energy Transition) work towards its aim of establishing a national energy data platform for planning purposes.
To enable semantic queries and interoperability with external tools, ontologies will be utilised and data will be primarily stored via knowledge graphs. This will also enable connections to external, conventional data sources, such as weather data, building data, geothermal resources etc.
This project is currently in progress. More information can be found via the Fortiss website.
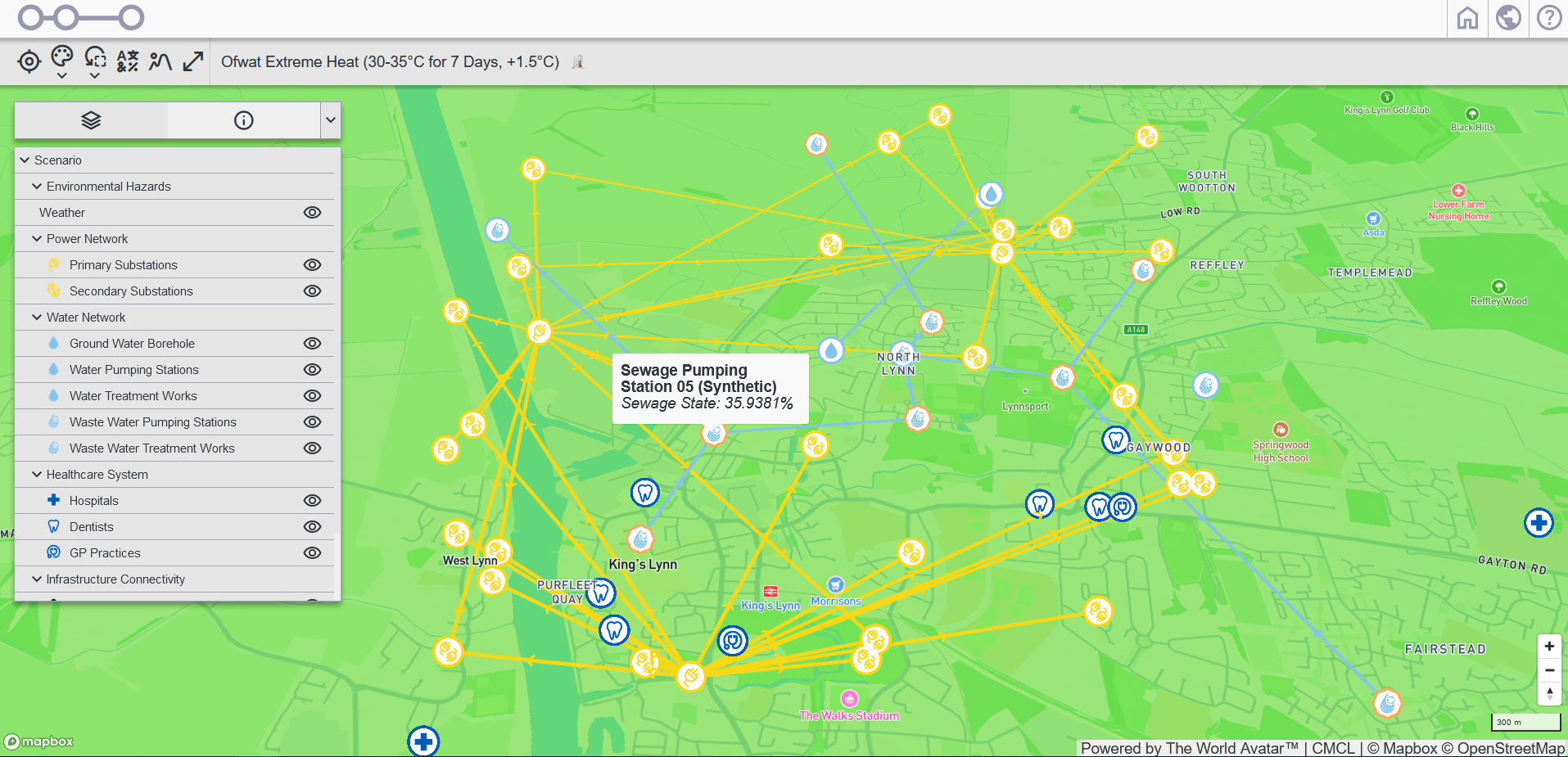
CReDo
The Climate Resilience Demonstrator (CReDo) is a innovative climate change adaptation project that provides a practical example of how digital twins and connected data can improve climate adaptation and resilience across infrastructure systems, and systems of systems.
CReDo looks specifically at the impact of flooding on energy, water, and telecommunications networks. It demonstrates how those who own and operate such networks can use secure, resilient, information sharing across sector boundaries to mitigate the risk of climate change and reduce the effect of flooding on network performance and service delivery.
CReDo is a collaborative project, with academic, industrial and governmental partners.
As part of the Ofgem Strategic Innovation Fund, it was recently awarded funding to integrate new partners and sectors – link.
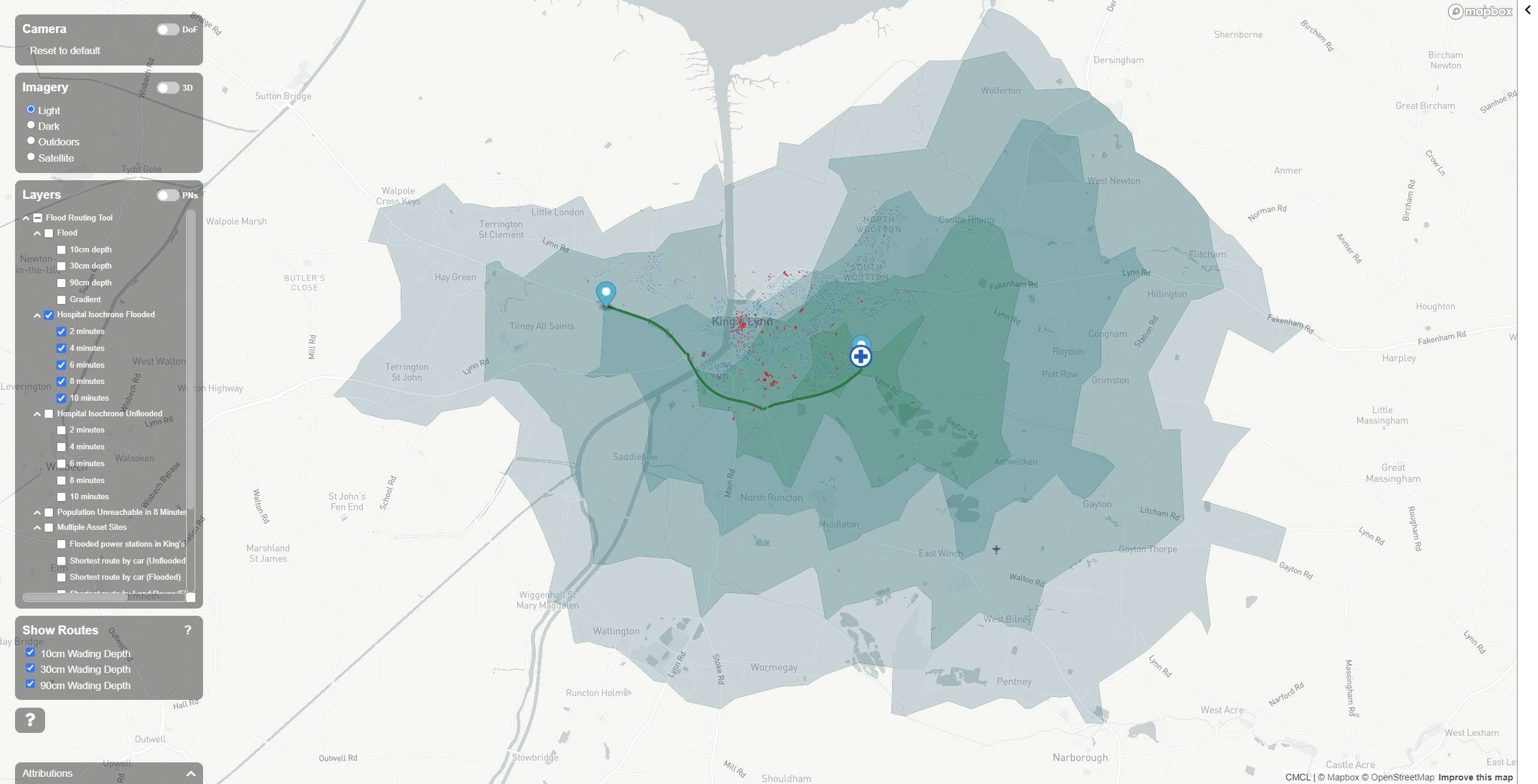
Flood Routing Accessibility
During this project (funded via a Transport, Research & Innovation Grant), CMCL connected a flood model with a transport modelling framework and population data to deliver a number of case studies:
- Hospital accessibility during a flood
- Impact of flooding on road usage
- Benefits of investment in emergency service wading vehicles
- Ability of infrastructure owners to service critical sites during flooding
A demo can be found via The World Avatar™ website.
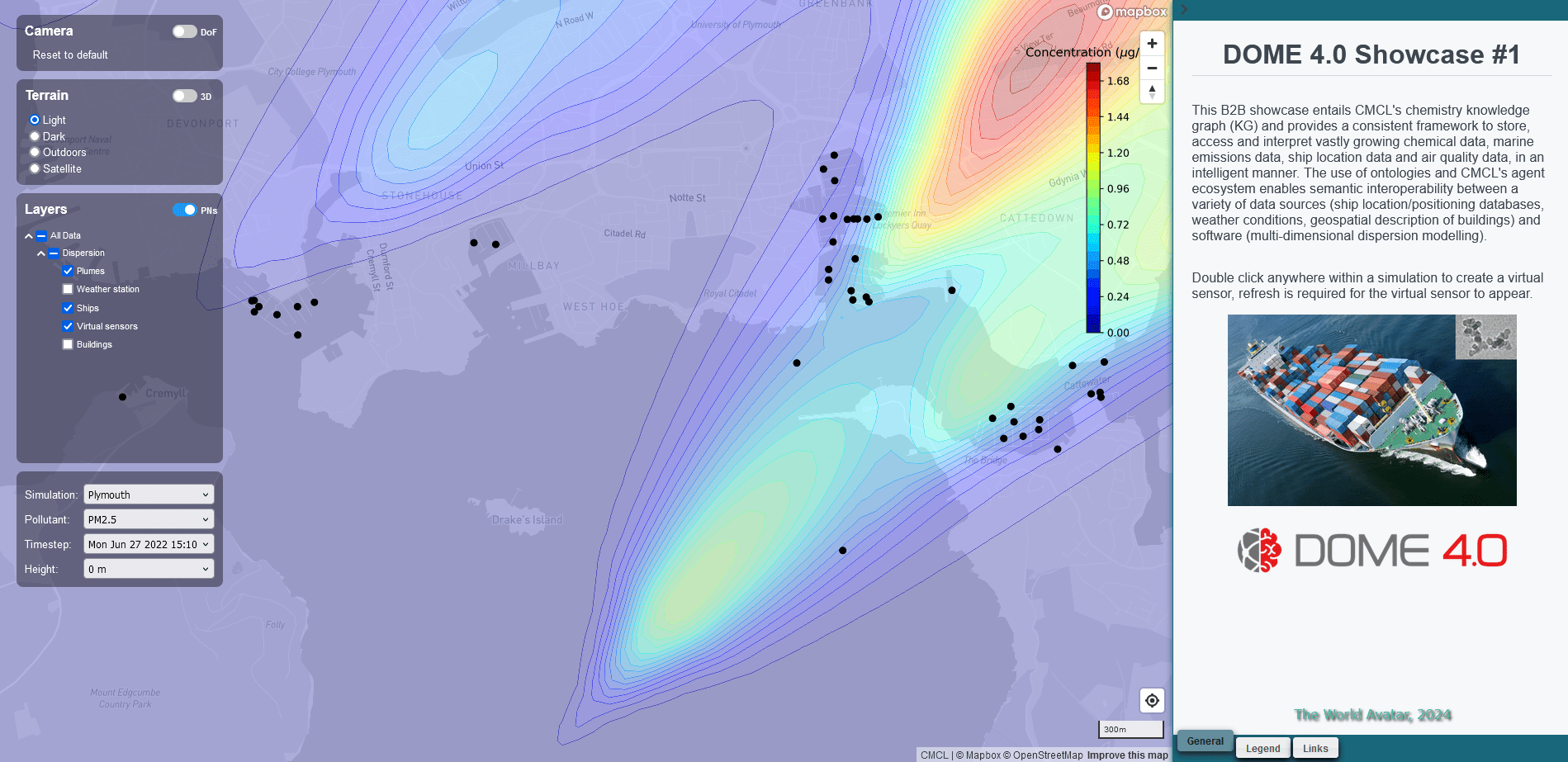
DOME 4.0
The Digital Open Marketplace Ecosystem (DOME) 4.0 offers an industrial data marketplace ecosystem based on Open Science and Open Innovation principles to enable sharing of business-to-business (B2B) data and creation of new or enhanced products, processes and services.
As project coordinator, CMCL’s showcase provides a consistent framework to store, access and interpret vastly growing chemical data, marine emissions data, location data and air quality data, in an intelligent manner using the DOME 4.0 ecosystem. CMCL established semantic interoperability between a variety of data sources (ship location/positioning databases, marine nanoparticle emissions software, air quality – dispersion modelling software, data-based surrogate model generation software). To achieve this interoperability across multiple domains CMCL leveraged and extended existing ontologies (Ontokin); detailed (mesoscopic and continuum) emissions prediction software, kinetics; and its data-based model development toolkit, MoDS.
Project website – link.

The Digital Lab Facility Manager
This work represents a novel framework for digitalizing and automating the management of specialized research laboratories using The World Avatar™. Semantic Web technology empowers users to effectively utilize data across various systems and formats without restricting them to a single software or protocol. Employing agents and ontologies, this work enables seamless data sharing, computational reasoning, and gradual automation of tasks, addressing obstacles in interoperability and adaptability.
Showcasing the capabilities of this approach, some common challenges in lab facility management were tackled, including cost-effective Internet of Things (IoT) sensor network integration with an existing building management system and efficient airflow management for fume hoods via “human-in-the-loop” interventions. Unified platform-agnostic interfaces were also developed that complement the framework. These advancements represent a significant stride in the holistic digitalization and automation of research laboratories at the nexus of fundamental science and smart building applications, setting a foundation for future research facilities to achieve operational excellence and sustainability.
Read more via the article.

Digital Pirmasens
CMPG have been working closely with local authorities in Pirmasens to support their digitalisation efforts across a range of key sectors:
- Ontological descriptions of land plots were used to allow companies seeking office space to not only search for existing space, but to identify land plots with suitable planning constraints for developers.
- An app was developed for the city, incorporating local events, citizen damage reporting and more.
- The utilities networks were geospatially represented via The World Avatar™. Operational savings were identified, and the digital groundwork built during this project will also support decisions made in the future.
- Buildings with the greatest heat demand and highest solar potential were identified as key targets for PV panel and heat pump installations
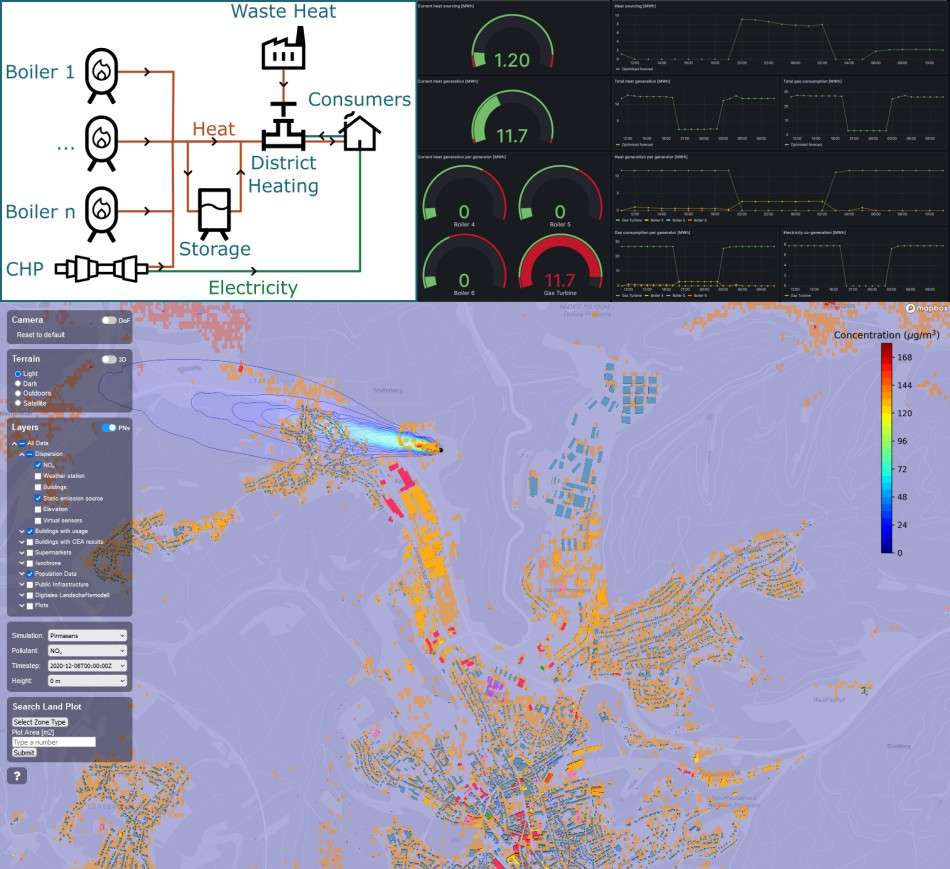
Smart District Heating
District heating systems typically produce heat with lower cost and carbon intensity when compared to domestic boilers. Most networks have very simple control systems. However, rapidly fluctuating demand, multiple sources of heat generation, and varying generation costs all increase system complexity. Within this project, ontologies were used to interoperably define the generation methods and connections, climate data, household demand and the energy market. Using this method, computational agents were able to more holistically optimise across the system. Connecting the electricity and gas networks then allowed for simultaneous optimisation across both, minimising overproduction and maximising waste heat utilisation.
What were the results? A 50% reduction in CO2 emissions and a 26% cut in OPEX.
“The successful collaboration between Stadtwerke Pirmasens (SWPS) and CMCL on this complex use case has paved the way for significant savings in operating costs and reduction of CO2” – Christoph Dörr, CEO SWPS
Going beyond traditional optimisation, the work was then connected to external sectors. By integrating population data, weather data and combustion models, the impacts of power generation on the local air quality were visualised. This work helps decision makers
DE-WASTE
DE-WASTE, or Digital Empowered Holistic Management and Recycling of Industrial WASTE, is a digital waste managmeent project in partnership with BNL, an environmental services company based in Singapore.
CMCL will be supporting BNL’s waste management division with operational insights. The waste management sector will be key to delivering and achieving net zero emissions, and due to its interactions with many other interconnected sectors, such as transport, energy and health, it represents an ideal partner for deploying The World Avatar™ approach.
Through this project, we aim to break down silos, further operational efficiency, connect to external sectors and build knowledge and expertise.
This work has been co-funded through a UK-Singapore Collaboration R&D grant from Innovate UK.


